How POS Systems Work A Complete Guide for Business Owners

How POS Works: The Tech Behind Smooth Transactions In Modern Trade
With transactions becoming faster, more secure, and easier thanks to point of sale (POS) systems, point of sale (POS) systems are evolving to adapt to the current fast-paced digital world. Whether you’re swiping your card at a traditional brick-and-mortar store, tapping your phone at a coffee shop, or scanning a QR code to buy something online, POS systems are what power these seamless and secure payment experiences behind the scenes. But just how do these systems work, and what technology makes them possible? In this post, we’ll dissect how POS systems work, the main integral factors that drive them, and how they’ve changed the game for transactions in businesses all over the world.
What is a POS system?
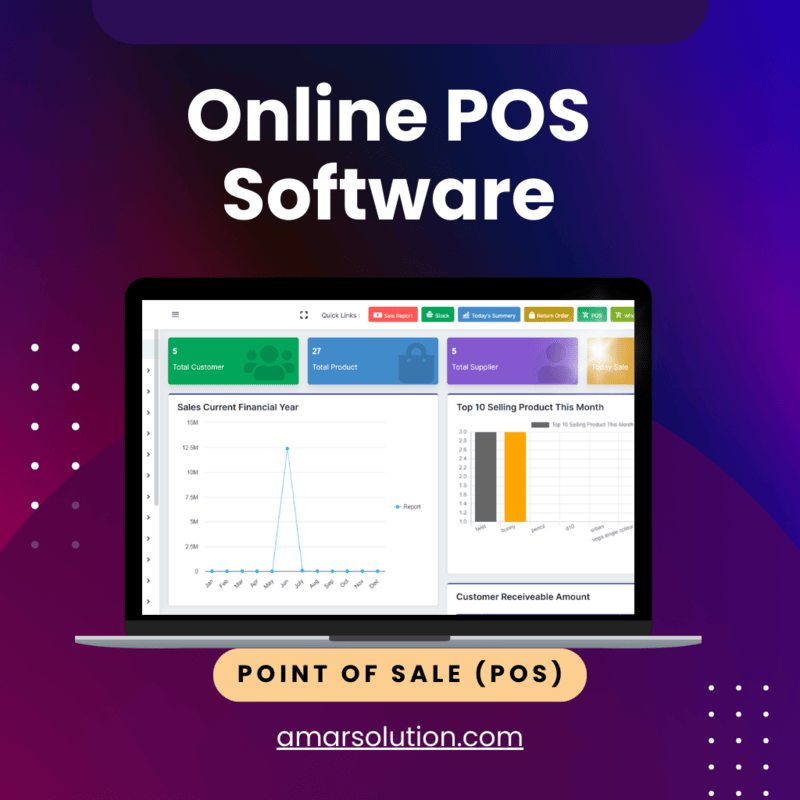
A POS (point-of-sale) system is the system that businesses use to complete sales transactions. The parts in which the customer pays money for something. This system could be as basic as what you would find with a typical cash register, or as complex as fully integrated cloud-based software that comes along with hardware (barcode scanners, receipt printers, card readers, etc.)
POS systems aren’t limited to retail; they also serve in many other industries, such as restaurants and cafes, hotels, e-commerce stores, and service-based businesses like salons or repair shops. POS systems are central to any organization in today's fast food business environment, as they enable one to carry on business transactions easily and effectively.
Key Components of a POS System
There are two parts to how a POS system works: the hardware and the software. Now, let’s discuss each of these in further detail POS systems Hardware describes POS devices used in transaction processing for businesses. These include:
Hardware:
- Card Readers: This allows people to swipe, insert, or tap debit and credit cards to pay for goods and services.
- Barcode Scanners: Utilized to rapidly scan product barcodes to acquire pricing and other product information.
- Receivers: The receivers are the printers used to give a hardcopy receipt to the customer after the transaction process is successfully done.
- Touchscreens: Touch-based POS systems enable cashiers to quickly enter items, apply discounts, and complete sales.
- Cash Cash Drawers - The actual cash drawer is used for cash transactions. They keep paper money and coins safe.
Mobile devices: Smartphones and tablets are alternative POS terminals when mated with the right software and hardware combination.
Software:
The POS system software serves as the brain of the system. It handles payments, sales, and inventory management all in real-time. Functionality of POS Software Some of the primary functionality of POS software includes the following: Point-of-sale: Includes features for the checkout counters.
- Sales tracking: The program tracks every sale, so business owners have an up-to-date view of what they're earning each day, week, and month.
- Inventory Management: Point-of-sale software allows a business to monitor and manage inventory, establishing when stock is too low so that new stock may need to be ordered.
- Reporting: Detailed Sales Forecast, Customer analysis, Financial Data, Equip businesses with data-driven decision-making by creating detailed reports on sales trends, customer behavior, and financial performance.
- Payment Processing: The tool lets companies accept payments on a secure platform through multiple channels such as credit cards, debit cards, mobile wallets, and even cash.
There are several newer POS systems that are cloud-based, with data stored on servers and accessed via the internet. This means they can offer flexibility, updates that happen automatically, and remote access so business owners can keep an eye on their shops from anywhere.
The Process of Payment: How POS Transactions Function
Here’s a look at the individual steps of a standard POS transaction:
Step 1: A customer makes a request for payment.
It starts when the customer takes action by attempting to buy The product will be scanned or entered by the cashier or customer.
2. Step 2: POS system computation:
After the items have been input, the system rings up the total and can calculate taxes, the exact amount owed and the amount of change due the customer.
Step 3: Payment Options:
There are a number of payment options for customers:
Credit/Debit Cards: Your patrons can insert, swipe, or tap their cards on the POS terminal.
Mobile Wallets: Payment is also accepted using mobile wallets such as Google Pay, Apple Pay, or Samsung Pay, in which you tap the customer’s phone or watch.
Cash: In-person shoppers can also pay in cash, and the POS system will handle change.
Step 4: Payment Authorization:
The POS system transmits the transaction information to either the payment processor or the bank for each card transaction. The bank checks the method of payment and that there is enough money.
Step 5: Receiving the Transaction After receiving the transaction, parties will confirm by:
When the bank has accepted the payment, the POS system receives an authorization approval indicating that the transaction is completed. In the case of mobile wallet or card payment, the customer usually gets a notification or SMS for a successful transaction.
Step 6: Finalizing the Sale
The POS software automatically adjusts inventory to account for the item sold, so inventory is always 100% accurate. If the business has a brick-and-mortar shop, a printed receipt is issued to the customer, or in the case of a digital business, an email confirmation is usually sent.
How the Technology Works in POS Systems
The POS system depends on a number of the latest technologies to facilitate the transactions smoothly. These include:
Cloud Computing: Among the benefits of cloud-based POS systems, it is possible to check data from time and any place. It allows companies to update and manage operations from afar, limiting the physical infrastructure required while delivering automatic updates. NFC is a two-way communication system between two electronic devices or a mobile phone and a receiver through a protocol of communication between devices by radio. Contactless payments can be accepted when NFC* technology is enabled for fast and secure payment methods that do not require physical contact between the card or smartphone and the POS terminal.
EMV Technology: The EMV chip card minimizes fraud risk by the implementation of a cryptographic process for each transaction. the security of these transactions is also relied on by EMV reducing the number of fraudulent transactions throughout the world, which makes payments more reliable.
QR Code Payments: QR codes have become a standard payment system, particularly with more and more people using mobile wallets. Customers may access the service by scanning a code printed on the POS with their smartphone.
The QR codes have entered popular culture as a form of payment thanks in part to the growing popularity of mobile wallets. With their smartphone, customers can use the service after scanning a code printed on the POS.
POS Transaction Security properties
Security is always a major factor in every financial transaction. POS systems are armed with multiple layers of security to safeguard sensitive customer data:
Encryption: Credit card information is encrypted during transmission and is unreadable by hackers or anyone else who may intercept it.
Tokenization: Tokenization replaces sensitive data—like a card number—with a unique identifier, or “token,” which adds an extra layer of security.
PCI Compliance: To protect against unauthorized handling of cardholder information, POS systems need to meet PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards) requirements. This is to help businesses guard customer information while transactions take place
The Benefits of POS Systems
There are several benefits of using POS systems for business:
Speed and Efficiency: POS systems shave valuable seconds off transaction times, which makes happy customers and leaves you with a more streamlined business.
Inventory Management: Real-time inventory tracking enables companies to control the stock levels and prevent overselling or out-of-stock situations of the product in demand.
Comprehensive Reporting: POS systems provide in-depth insights into sales, customer actions, and trends, allowing businesses to make informed decisions.
Enhanced Customer Experience: POS systems can be tied to loyalty programs, promotions, and discounts, providing customers with a more customized experience.
Where POS Systems are Used
POS systems are integral to a wide array of industries, allowing businesses to streamline payment processing, track inventory and improve customer service. While point of sale systems are commonly found in the following areas:
Retail: POS systems are used in places like small boutiques and large department stores to process sales, track inventory and produce sales reports. They enable businesses to simplify the checkout process so it is faster and easier.
Restaurants and Cafes – In the F&B sector, POS helps with the convenience of taking order, processing payments, not to mention it can easily integrate with kitchen orders. They also speed up billing and order tailor-made offering for an improved restaurant visit.
Hotels and Resorts: In hotels and resorts, a POS system is used to manage guest room charge, check in, room check out, room charge, restaurant billing, and other services. They provide fast billing and payment for their front-office and back office business.
Healthcare – Hospitals and clinics also take advantage of POS as it can assist in handling patient billing, insurance claims and prescriptions. They simplify the payment transactions and minimize errors, thereby increasing the efficiency of medical practices as a whole.
E-commerce: To online storefronts, POS systems connect to websites to process payments, monitor stock, and trace customer sales, maintaining smooth shopping experiences and readily available information.
Beauty Salons and Spa: POS systems can track bookings, payments, and inventory, streamlining the management of bookings and customer services in beauty salons and spas.
Pharmacy: In pharmacy outlets, customers are attended with the help of POS systems to get the right prescribed medication, monitor stock levels and manage claims to insurance companies and billing.
Transportation: Transportation businesses such as taxis, buses, and car rentals leverage POS systems for ticket sales, reservation, and payment.
The Future of POS Technology
With further development of technology, POS systems are becoming more and more complex. Mobile POS systems are on the rise and now enable businesses to finally accept payments on the go and on the fly with smartphones and tablets. Furthermore, POS systems now include artificial intelligence and machine learning to allow businesses to analyze data on customers, predict purchase trends, and perform tasks such as inventory management automatically.
Conclusion
Systems like a POS system have redefined how businesses execute transactions, which are easier, safer, and faster. Knowing about how POS systems function and the technologies that drive them, can help entrepreneurs capitalize on their efficiencies and execute improved customer service. Whether you are a retailer business owner like a shop or an ecommerce owner like an online store, you need an excellent POS to enable you keep pace with the travails of contemporary commerce.
If you need to simplify payment and maximize business efficiency, the POS is ready for you. Contact us here at AmarSolution!